|
Throughout this site we use many technical terms, and given the breadth of readership our site enjoys, sometimes we are remiss and incorrectly assume everyone knows what we are referring to. For those that do not, here are some explanations of the technical terms use. |
 |
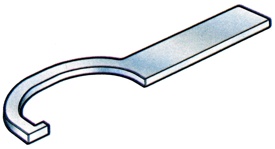
Spanner whose head is in a hook or C shape to engage in a slot cut in a circular component. |
 |
A strong wire of twisted steel strands used to operate parking brakes, accelerator, choke and other operations where a strong, flexible, movable connection is required.
|
 |

Originally a French term, but now used widely by all manufacturers to describe soft-top or convertible style automobiles. A motor car with a roof (or part roof) designed to fold back, leaving the side windows in position. |
 |
A projecting lobe on the periphery of a wheel used to convert circular into reciprocal (or variable) motion. |
 |
A term used to describe the off-vertical 'set' of the wheels of a vehicle. The convex bow on a road surface to drain water to the sides |
 |

A revolving shaft on which is set a series of cams designed to operate various mechanical movements such as the operation of the inlet and exhaust valves of a car engine. Driven off the crankshaft, the camshaft consists of a series of machined eccentric lobes that open and close the valves, thus controlling gas flow in and out of the cylinder head. Camshafts have the job of opening the valves and allowing the fuel/air mixture in, and then opening another set of valves to allow the burnt gases out. Different camshafts open the valves for different periods of time (duration), and push the valves open a certain distance (lift). The standard camshaft fitted to most of today's cars is a compromise. Manufacturers fit cams which give a reasonable rev range without sacrificing too much torque, and vice versa.
What you want your car to do will determine the type of camshaft you fit. For a car that will be used for track work, a full race cam would be the best bet. This would allow the engine to breathe deeply at the top end of the rev range, but would sacrifice bottom end grunt to the extent that the car would probably need a big serve of revs to get it moving. A car that was to be used towing heavy loads would be better fitted with a completely different camshaft. That car would need a relatively low profile cam which would give masses of torque at low engine speeds needed to get a load moving and keep it moving up hills.
You can specify either a billet camshaft and have it ground to your own specifications, or have the camshaft already in your car reground for a better profile. In either case, specialist help will be needed to determine the correct duration and lift. Simply returning the camshaft to its standard specifications in older cars can sometimes provide a performance boost. Cams, like any other engine components, are subject to wear. The wearing process can gradually grind down the lobes, allowing the valves to stay closed more than they should. Holden's 308 V8 engines are notorious for such wear, which occurs when the hardening agent on the lobe surface breaks down. |
 |
Produced by the burning of fuel and oil in the combustion chambers of the engine and deposited on cylinder head, piston crowns, valves. |
 |
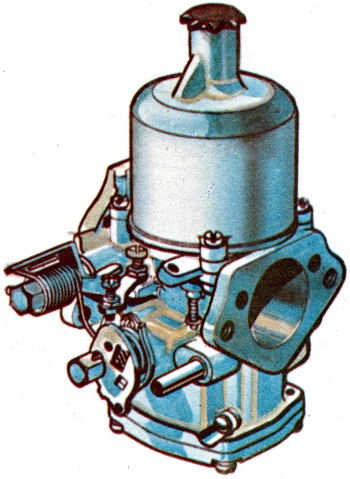
A fitment to a motor vehicle engine designed to mix air with petrol vapour in correct proportions for combustion in the engine. It is controlled by the choke and accelerator. |
 |
The term sometimes applied to the crimped paper filter used inside the air or oil filter containers. |
 |
A metal part not fabricated but formed into its shape by pouring molten metal into a mould. It is normally machined afterwards eg the engine block or cylinder head. |
 |
The ability of a car's steering geometry to tend to straighten the steering wheels after a turn to left or right. |
 |
A contrivance for checking the motion of a door, etc. |
 |
The negative pole of a battery or circuit. |
 |
A manufactured chemical paint normally used in spray painting metal or woodwork and capable of giving a weather resistant high gloss. |
 |
Applied to bodies revolving around a centre with use made of the tendency such as in some clutches or governors (regulators). |
 |
A connected series of hinged metal or other links used in a vehicle to transmit power. |
 |
An enclosed space in the body of a machine such as the combustion chamber of a cylinder in a vehicle's engine. |
 |
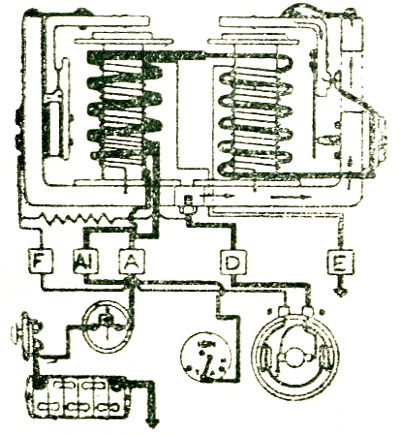
The main charging circuit carries current from the generator / alternator to the battery. The circuit can be traced below; the current flows from the generator armature to the "D" terminal on the generator. This terminal is connected to the "D" terminal at the control box, and a metal connecting strip joins the "D" terminal to the "L" shaped regulator frame, causing the frame to be at generator potential. Heavy lines show the main charging and load circuits. |
 |
The auto frame with all operating parts including the engine, suspension and brakes. |
 |
A machine for measuring the amount of power delivered to the drive wheels of a car. |
 |
A valve which allows passage of a liquid or gas in one direction only. |
 |
A restriction in a carburettor throat to reduce airflow during cold starting and engine warm-up. |
 |
A coupling by which moving parts may be made to engage or disengage at will. |
 |
The rotating circular metal plate splined to the transmission input shaft; it has friction material on each face. |
 |
A toothed belt normally of fibre-glass reinforced rubber for driving the camshaft from the crankshaft. |
 |
A pulse transformer designed to step up the low 'primary' voltage received from the battery or alternator/ generator to approximately 20,000 volts upon the opening and closing of the contact points. |
 |
Type of clutch in which the operating pressure is provided by a series of small coil springs arranged round the perimeter of the clutch plates.
|
 |
System of suspension using coil springs at each wheel. |
 |
Welding system in which the two ends to be joined form the contacts for an electrical current which melts the ends sufficiently to join them. The system is so called because only the metal in the immediate area of the weld becomes hot. It is usually used for joining strip. |
 |
Steering column designed to distort under pressure to absorb impact forces which might otherwise cause injury to the driver. |
 |
Steering wheel whose rim buckles under impact to absorb impact energy, thereby avoiding injury to the driver's chest. |
 |
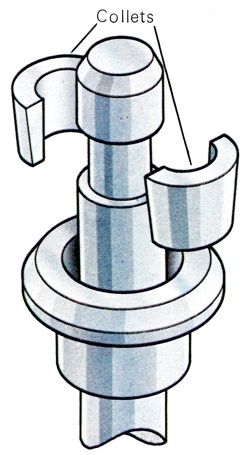
Collets Metal keys to secure one component to another. The most common type of collet is found on valve stems where half-conical steel items fit into a recess cut into the valve stem and are retained by the pressure of the valve spring. |
 |
Compound containing a proportion of abrasive designed to lift a thin skin of dirty, oxidized, paint from the surface of the bodywork finish. |
 |
Slender lever fitted to the steering column to allow finger-tip control of such items as lights, direction indicators, horn and windscreen washer, without the driver having to move his hands from the steering wheel. |
 |
The burning of the mixture of petrol vapour and air introduced into the engine through the carburettor. |
 |
Recess in which the combustion process takes place. In compression-ignition and some petrol engines, the recess is in the piston crown, but usually it is in the cylinder head. |
 |
Copper segments, separated by insulating strips, fitted to a drum and connected to the armature coils of a DC generator or motor. In a dynamo, carbon brushes bearing against the segments carry the electrical current generated by the dynamo to the battery. In a motor, electrical energy from the battery is carried through the brushes to the commutator to drive the motor. |
 |
(CVC) Automatic regulator fitted between the car's generator and battery to regulate the voltage applied to the battery. |
 |
Port in a two-stroke engine which delivers fuel mixture from crankcase to cylinder when the pumping action of the descending piston puts the crankcase under pressure. It is often known as the transfer port. |
 |
The pressure existing in an engine's cylinder when the piston is at the top of its stroke with both valves closed. At cranking speeds, the compression in an average car's engine is in the region of 9 bar (130 psi). |
 |
Device for measuring the compression in an engine cylinder. |
 |
Internal combustion engine which is fired by the heat generated by highly-compressed air and not by sparkplugs. Such engines have compression ratios twice to three times as high as spark-ignition engines. |
 |
A calculated ratio that relates the uncompressed volume of the cylinder with the piston at bottom dead-centre to the compressed volume of the cylinder with the piston at top dead-centre. Hence a 9:1 compression ratio means that the air-fuel mixture is compressed to one-ninth of its original volume before being ignited. The compression ratio bears little relationship to the actual effective pressure created in the cylinder. Can also be described as the ratio between the volume of the cylinder above the piston when the piston is at BDC (including the volume of the combustion chamber) to the volume when it is at TDC (that is, the combustion chamber only). Expressed as a formula, compression ratio is: cv + sv / cv where CV equals clearance volume and SV equals swept volume. |
 |
The piston ring fitted to the top groove or grooves of a piston. This flexible ring is designed to prevent leakage of gas past the piston and the cylinder wall.
|
 |
The second movement of the piston in a four-stroke cycle, the piston rising to compress the induced fuel mixture with the inlet and exhaust valves closed. |
 |
Compression Tester
See Compression gauge. |
 |
Form of air-pump to supply air at high pressures for inflating tyres and operating air tools. Compressors are usually garage equipment although lightweight units, powered by mains or battery, can be bought for home use. Some types of air compressor work from the engine on commercial vehicles. |
 |
Formation of water resulting from temperature differences. The most commonly found types of condensation are the misting of car windows in cold weather and the film of moisture occurring on ignition leads. Condensation also occurs inside a car engine and exhaust system on a cold night when the hot engine cools and is made evident by water dribbling out of the exhaust pipe, or by steam when the engine is re-started. No corrective action is necessary. |
 |
|
 |
Plastic, rubber or metal tube (or sleeve) carrying electrical wires to protect them from mechanical damage or heat. |
 |
Early form of clutch, usually leather-faced, abandoned in favour of the plate-type clutch by the early 1920s. |
 |
The simplest form of synchromesh is now rarely used but it illustrates the principles on which many of the more sophisticated systems operate. The side of the gear to be engaged has two features. First, it has a hollow cone and second, the cone is surrounded by a ring of dog teeth. The cone and the teeth are the components that the synchromesh mechanism contacts when a gear change is made. |
 |
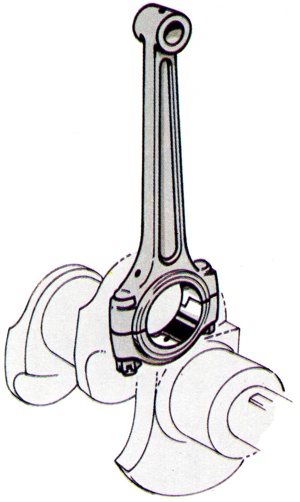
Rigid H-section forging or casting, usually made from alloy steel, which connects the piston and crankshaft. The cranks aft end terminates in a large split bearing (the big-end bearing) which fits closely round the crankpin, while the upper end includes a much smaller bearing (the little-end, or small-end, bearing) fitting round the gudgeon pin secured to the piston. |
 |
Battery-charging method in which an unchanging amount of current flows into the battery, in contrast to the variable amount in constant voltage charging. |
 |
Gears which do not move in relation to one another when the driver changes gear, but are continuously meshed, gear changing being affected by the movement of dog clutches in the synchronizing unit. |
 |
Constant Vacuum Carburettor
See variable-jet carburettor. |
 |
Type of universal joint fitted to front-wheel-drive systems. |
 |
Battery-charging method in which a constant voltage is applied to the battery, and the current input is progressively reduced as the battery approaches a fully-charged condition. |
 |
That part of a tyre in physical contact with the road when the car is moving. In the average saloon, the contact area of each tyre is roughly the same size as the sole of a shoe. |
 |
In conventional ignition, the automatic switch formed by the contact-breaker points in the distributor which are forced apart by 'humps' on the distributor shaft bearing against a fibre block on the contact breaker arm. Spring pressure closes the points after the 'hump' has passed its peak and the make-and-break pattern established switches on and off the flow of electricity in the primary winding of the coil. |
 |
Metal 'pips' on the contact breaker blades of a conventional distributor which open and close the ignition primary circuit.
|
 |
Unit which balances the output of a dynamo to match the demands on a battery so that its state of charge is maintained. |
 |
Type of bodywork construction in which the roof is collapsible to offer open-car facilities in hot weather. |
 |
The cooling medium in a water-cooled system, including antifreeze and/or other additives. |
 |
Arrangements to regulate the operating temperature of the engine. Cooling systems are most often of the water-cooled type, although many cars have air-cooled systems in which cold air is blown through fins cast on to the cylinders to dissipate the heat. |
 |
Textile threads or steel wires woven into the plies from which a tyre is made. Tyre damage causing these cords to fracture means the tyre cannot be repaired. |
 |
Passage left in the cylinder block and head in the casting process. Cores are used as part of the cooling system. Also the inner portion of a tyre valve stem, consisting of a spring-loaded valve with a nylon head bearing on a seating to retain air inside the tyre. The valve is forced off its seating by incoming air under pressure to inflate the tyre and returns when the air-line is disconnected. |
 |

Metal disc which seals off the end of the core left in the cylinder block (and, sometimes, cylinder head) by the casting process. The core plug can also act as a crude form of safety device against frozen-up cooling systems, by allowing the freezing water to expand and force the core plug out of the block, thus preventing the forming ice from cracking the block. |
 |

Sideways force exerted by the tyres when the steering is out of the straight-ahead position. It is the resistance of the tyres to the road surface that allows the car to be steered. The extent of the force varies widely with the condition of the tyres and the road surface. |
 |
Usually, decay of the metal parts of the car caused by rust. The word also covers excessive wear by other means, including electro-chemical action on battery connections and other points of electrical contact. |
 |
Metal or plastic key fitting into a slot or hole to join two components. The pin may be wedge-shaped to give an interference fit, or rely on external pressure to hold it in place, as with a collet. |
 |
Gear shaft used to balance another gear shaft. One example is the countershaft found in V-four engines to balance the out-of-balance forces produced in the crankshaft. Also an alternative name for layshaft. |
 |
Type of bodywork construction in which the rear part of the roof slopes more sharply than in a saloon to give a sporting appearance. |
 |
Interior light which is automatically switched on as the car's doors are opened to assist passengers entering and leaving the car in the dark.
|
 |
U-shaped rod by which the rotary movement of a rod or shaft is converted to an up-and-down movement, or vice versa. A crank can be used to increase the torque available through a shaft, as with a brace and bit, wheel-nut wrench, starting handle or jack-handle. |
 |
The lower part of an engine, accommodating the crankshaft and acting as a reservoir for the lubricating oil. |
 |
The presence of undesirable foreign matter in the crankcase, affecting the efficiency of the lubrication of an engine. Such elements include water, petrol, acids and carbon. Crankcase dilution is usually the result of an engine fault or an over-cool engine. |
 |
Device allowing the escape of excess pressure in the crankcase, usually caused by defective piston rings allowing gases to pass down the cylinders. |
 |
Offset part of the crankshaft carrying the big-end bearing part of the connecting-rod. |
 |
Advanced and serious scoring of a crankpin, usually resulting from extreme wear of the big-end bearing or the presence of grit in the lubricating oil. |
 |
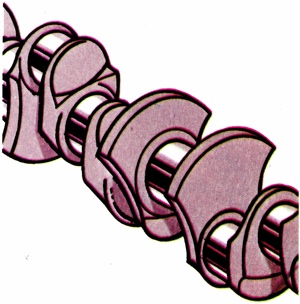
Assembly in the lower part of the engine carrying the crank-pins to convert the reciprocating movement of the pistons into a rotary motion to power the transmission system. |
 |
High-precision measuring device to gauge the 'truth' of the crankpins and main-bearing areas of the shaft. |
 |
Gearwheel or sprocket attached to the crankshaft and driving such ancillaries as the camshaft(s), injection pumps and fuel pump and, indirectly, the distributor drive and oil pump. |
 |
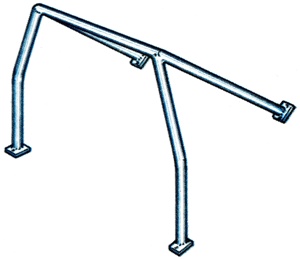
Safety arrangement found in competition cars and consisting of a bar or strut fixed in the roof area to prevent the occupants being crushed in the event of the car rolling over. |
 |
Obsolete type of gearbox, now superseded by the synchromesh version. |
 |
Safety programme in which hard, rigid, components in a car, such as sun-visors and instrument panels, are replaced by softer or collapsible items. |
 |
Loose expression to describe a speed at which the behaviour of a car or certain of its components may become unpredictable. For example the critical speed of a car - which varies widely according to road conditions - is the speed at which control may be lost. |
 |
Spring loaded clip with heavily toothed jaws used to make a temporary electrical connection.
|
 |
Radiator whose cooling tubes are arranged so the coolant flow is from side to side rather than from top to bottom. Such radiators are often fitted where bodywork design precludes the use of a gravity-type radiator, for example to lessen wind resistance in sports cars. |
 |
A transverse stiffening member on the underside of a car. |
 |

Tyre in which the cords in each ply are oblique to the circumference. More accurately described by the American term bias-ply tyre. |
 |
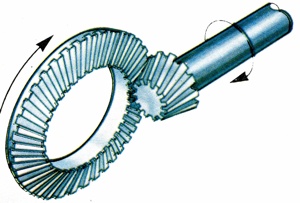
Final-drive arrangement in which a large bevel wheel (the crown wheel) engages in a smaller bevel (the pinion) so that the direction of the rotation of the propeller shaft is turned through 90� to drive the road wheels. |
 |
Sections of a car at the front and rear and, in some cases, the sides, designed to crumple under impact thus absorbing energy which would otherwise be transferred to the occupants and possibly cause injury. |
 |
Bodywork restorer's term for the use of a mild abrasive to restore the colour of faded paintwork. |
 |
Part of a charging control system which prevents the current in the battery flowing back into the generator when the engine is switched off or running too slowly to produce a charging voltage. |
 |
Abrasive paste used by bodywork specialists to restore faded paintwork or eliminate blemishes in a sprayed surface. |
 |
Spring or split washer whose perimeter has been cut at one point and the ends sprung slightly away from each other to give a locking effect when used between a nut and bolt. |
 |
Series of repetitive stages. In automotive engineering, the term is most commonly used of the two-stroke and four-stroke series of operating stages. |
 |
Opening in an engine block in which a piston moves up and down. |
 |
Iron or light-alloy casting in which the cylinders are accommodated. |
 |

Iron or light-alloy casting which fits tightly to the cylinder block and contains the combustion chambers, valves, valve seatings and spark-plugs. An efficient cylinder head will improve performance more than would be expected by many people. With no moving parts other than the valves, the cylinder head is involved in all aspects of a four stroke engine's operation - induction, compression, ignition, and exhaust. One way of improving a cylinder head is called porting and polishing. This very time consuming process enlarges and maximises the finish of the intake and exhaust ports, and allows a more efficient flow of gas. Big valves and multi-valve heads are also beneficial as they improve swirl patterns of the fuel/air mixture in the combustion chamber and thereby increase the amount of fuel that is burnt and turned into horsepower. A head can also be shaved — that is, a few thousandths of an inch of metal are scraped from the head surface to reduce the space in the compression chamber, raising the compression ratio and power in most cases.
Cylinder heads can also be fitted with roller rockers. Roller rockers take the place of the standard cast iron rockers which transfer the movements of the camshaft, through the pushrods, to the valves (in an overhead valve engine). When the camshaft lobe lifts a pushrod, the rocker is forced to rock — hence the name — and open a valve. Cast iron rockers, while cheap to manufacture, have inherent problems. They are prone to breakage during extended periods of high engine speeds. They also scrape across the valve tip during the opening process, a method which causes a great deal of friction, heat, and can shorten the lifespan of valves and valve guides. Roller rockers, on the other hand, actually have a roller bearing in their tip, which rolls across the valve tip, drastically reducing friction. |
 |
Thick washer fitting between the cylinder block and cylinder head to absorb minor manufacturing imperfections, act as a slightly-flexible seal to accommodate differing rates of expansion and provide a gas-tight and water-tight seal between head, block and cylinders. In some engines, there is no head gasket as such but waterproof washers are fitted in the waterways. |
 |
Rotating set of carborundum stones used for the finishing of engine rebores after the ridge remover has done its job. It is also used for the removal of glaze, and small scores in the cylinder walls. |
 |
|
 |
Sleeve fitted to a cylinder block to enclose a piston. Cylinder liners are used in all light-alloy blocks and some iron blocks. Wet liners have the coolant coming into direct contact with their exteriors while dry liners bear against the wall of the water jacket. |
|
| Sell Your Car or Parts Browse the Classifieds It's Absolutely Free! - Find Out More |



