|
Throughout this site we use many technical terms, and given the breadth of readership our site enjoys, sometimes we are remiss and incorrectly assume everyone knows what we are referring to. For those that do not, here are some explanations of the technical terms use. |
 |
Used in conjunction with some coil spring rear axle set-ups. This type of location bracket stops the axle moving back and forward in relation to the body of the vehicle. The 'apex' of the "A" is fixed to the differential while the 'legs' of the "A" are fixed to the axle.
|
 |
|
 |
Front-most pillar in vehicle body construction that joins the roof to the lower portion of the body. Successive pillars are called B, C and (with wagons) D. |
 |
After bottom dead centre (see Bottom dead centre).
|
 |
Ability of (especially) a motor tyre to resist wear, as distinct from cutting or tearing. Abrasion resistance is often improved by incorporating carbon black within the tyre rubber. |
 |
A substance - for example, sand, glass or grit - used for cutting, grinding or polishing a surface. |
 |
|
 |
Foot pedal, inside the car, used to control the accelerator pump. Accelerator is also an alternative name for the catalyst in a chemical reaction, especially the curing of paint or plastics. |
 |
A pump in the carburettor which enriches the fuel/ air mixture as the accelerator is depressed. It is either piston- or diaphragm-operated. Attached to the carburettor body, it performs the specific function of negating the lean-out effect caused by sudden large throttle openings. It is activated directly off the throttle cable (or linkage) via a diaphragm arrangement and nozzle. Sudden throttle openings activate the diaphragm which forces petrol through the nozzle into the carburettor throat. On slow throttle openings, there is a bleed-by arrangement that allows the fuel to return to the pump bowl rahter than being forced through the nozzle. |
 |
Devices - for example, mirrors, radio, heater - which are not essential to a car's operation but enhance its safety, comfort or performance. |
 |
Rechargeable battery, usually of the lead/acid type. |
 |
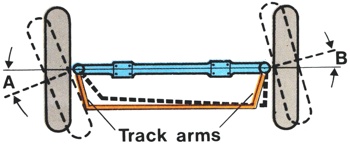
Steering system in which the track rod is shorter than the distance between the king-pins, causing the inner wheel to turn through a greater angle than the outer wheel when turned. When vehicle is travelling straight both wheels are parallel to each other. When the wheels are turned a difference in wheel angle occurs and increases as more lock is applied. |
 |
|
 |
Fitting for connecting together components of different sizes, eg, different sized pipes. |
 |
Substance added to fuel, oil, brake fluid, cooling water etc to improve its performance. There are two types, oil and fuel. Oil additives make up about 15% of oil volume and are used to inhibit oil oxidisation (the main reason for oil breakdown) and to clean carbon deposits (detergent additives). The main fuel additive is teteathyl lead which is used for its anti-knock properties; its addition allows octane levels to be dropped without fear of creating mechanically dangerous pre-ignition or pinging. |
 |
Single spanner that can be altered to fit nuts of different sizes by the use of one fixed jaw and one parallel sliding jaw. The two main types are the 'parrot jaw', whose jaws are slanted as in a normal spanner; and the 'king dick', whose jaws are at right angles to the line of the handle, producing a wider range of jaw sizes. |
 |
The moving ahead of the ignition spark so that an engine fires before the piston reaches top dead centre. Also, the amount in degrees by which the ignition spark has been advanced. |
 |
This refers to the change in ignition timing that is made through both mechanical and vacuum systems to allow for different combustion situations for different rpm and smaller or larger throttle openings. The mechanical system advances the ignition as rpm increases to allow for the decreased time for combustion. |
 |

Science of the effect of air on a body moving through it. The study of physical forces at work when a body passes through the air. In the automobile world, the term aerodynamic drag is used to describe the resistance that the air exerts on a car moving at speed. By changing the body shape of a car to reduce dynamic drag, the energy output of the engine can be better utilized either in the form of reduced fuel consumption or improved performance. The French auto manufacturer Citroën pioneered the development of aerodynamic passenger cars with the DS19 in 1955, and have remained leaders in this field. |
 |
Cooling fan with sprung blades whose pitch reduces as the engine speed increases. It is designed to prevent over-cooling of an engine at high speeds. |
 |
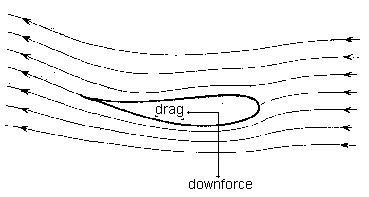
Also termed “wing” or “wings”, these devices were first fitted to race cars to to increase down-force and thus traction at high speed. The greatest benefit, apart from keeping the car firmly on the road, is to allow higher cornering speed. |
 |
Can, for paint and other liquids, incorporating its own supply of high-pressure propellant. The propellant forces the paint through the nozzle when downward pressure on the valve opens the spray nozzle. |
 |
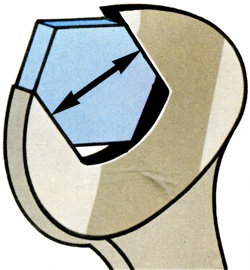
Widely-used system of measuring nut sizes. Nuts and bolt-heads are measured by the distance between the jaws, or flats, of the spanner needed to turn them. This is an alternative method to that of measuring the thread size of the bolt. It is usually quoted as, for example, 7/8" A/F. |
 |
|
 |
Boiling of the cooling fluid in the engine, or of fuel in the carburettor, after the engine has stopped. |
 |
Type of exhaust manifold that burns hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide in the exhaust gas as a means of reducing air pollution.
|
 |
Balloon-like safety device that opens automatically in a car accident to prevent the occupants from being thrown violently forward. |
 |
In fixed-jet carburettors, a small hole or jet used to add extra air to the fuel/air mixture. The main types are the pilot air bleed which produces a weaker air/petrol emulsion for idling, and the main air bleed which reduces over rich mixture up to full throttle. |
 |
Small screw allowing unwanted air in a sealed fluid system to escape. |
 |
Another name for Air bleed screws, on hydraulic braking and clutch system. Also part of a system of using air from the engine for the car heater. |
 |
Brake system using compressed air in place of hydraulic fluid to supply the necessary effort to operate the brakes. |
 |
|
 |
Engine using air as a cooling system. The air is fan-driven across heavily finned cylinders and heads. The fins are usually made of aluminium alloys and increase the heat-dissipating area. Air-cooled engines are usually run at higher temperatures than water-cooled and so need larger bearing clearances. Due to the absence of the sound baffling water jackets they are also usually noisier. |
 |

An aerodynamic aid placed across the lower nose of the car to prevent the energy consuming and dynamically un-stabilising effect of air being forced under the car. Device fitted as low as possible at the front of the car with the object of forcing more air round the car and less underneath, thereby creating a measure of downforce, reducing aerodynamic lift and increasing straight-line stability. |
 |
Unit used to remove foreign particles from the air and fitted at the air intake. The most common example is that on the carburettor. |
 |
Mixture of air and fuel, combined in the carburettor, that is drawn into the combustion chamber and ignited to provide the motive power of the engine. |
 |
Comparison of petrol/air quantities in the Air/fuel mixture, usually measured by weight. Fifteen parts of air to one part fuel is a typical ratio. |
 |
Small gap between electrically related parts, for example, the spark-plug gap, or magnetically related parts as in, for example, the alternator. |
 |
Warning device powered by compressed air, or by reduced air pressure in the inlet manifold which sucks air through the horn |
 |
System which completes the combustion of carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons in the exhaust gas by injecting air into the exhaust manifold or a thermal reactor. |
 |
Pipe or hose through which air passes. |
 |
Inhibiting effect of air pressure and inertia on a moving surface. It increases as the square of the speed of movement. |
 |
Suspension system using compressed air as the damping medium. Citroen D series cars are typical examples of vehicles with air-suspension, incorporating self-levelling. |
 |
A small hole, allowing atmospheric pressure to be applied, found in the brake and clutch fluid reservoirs and also on the carburettor float chamber.
|
 |
The pressure which returns a tyre to parallel with the body when it has been turned for steering. |
 |
The normal setting for the front wheels of a car, usually parallel to each other and to the body axis. Headlamp beams are also adjusted to a normal setting or state of alignment. |
 |
Clamping device similar to the Universal clamp, but with a pull plate providing a much more definite point of pulling. Four positions on the clamp allow a variety of pulls to be exerted without undoing and repositioning the clamp segment. |
 |
Two-shaft gearbox (as opposed to the normal three-shaft) in which the drive passes through two gears in every ratio, one on the input shaft and one on the output. Top gear hence does not have the direct drive of a conventional gearbox. |
 |

Piece of high tensile steel hexagon bar with a right angled bend. Either end is fitted into the socket in a hexagon socket head screw and used as a lever to rotate the screw. Allen keys come in a range to match screw sizes. |
 |
Manner of connecting two transistors in alternator voltage regulators. |
 |
Electric current that continuously alternates from positive to negative current flow. |
 |

Generator, used in most modern cars, which produces alternating current and then converts it to direct current, as opposed to the dynamo which produces direct current. The alternator produces a higher output than the dynamo at low engine speeds.. A device fitted to the engine to convert mechanical rotational energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy is stored in the battery and used to operate the various electrical functions of the car. |
 |
Stiff lacework of aluminium wire used in repairing holes in a curved section of bodywork. It is pre-shaped to the contours of the existing section and stuck over the back of the hole, using filler to stick it in place. |
 |
The American system of defining bolt and screw-thread sizes. |
 |

An instrument for measuring electrical current and hence the electrical output of the alternator. Instrument indicating the charge being put into the battery by the generator, also measuring the current being used by accessories, eg lights, heater, radio. Usually reads from + 30 through zero to -30 amps. A positive reading shows the battery being charged, a negative reading shows the battery draining. |
 |
Measuring unit of electric current�the amount produced by 1 volt acting through a resistance of 1 ohm. Usually shortened to Amp. |
 |
Measuring unit obtained by multiplying current in amps by time in hours for which it flows. A typical car battery uses 38 Ah. |
 |
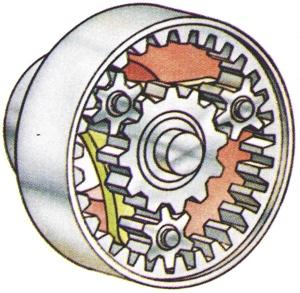
The outer ring of an Epicyclic gear. It consists of a ring with the teeth on the inside circumference. |
 |
Surface hardened, corrosive resistant aluminium used for radiator grilles and other decorative finished parts of the car. |
 |
Aerial rod, connected to the radio, used to pick up radio signals. It is usually situated outside the car, on a wing or on the roof. |
 |
Specially designed lock that resists opening under impact, particularly from a crash. |
 |
Devices used to eliminate headlamp glare which causes danger to oncoming traffic. Two main features are incorporated: 1. The beam direction is changed by directing the current through the upper, dip, filament. This reflected light is refracted (bent) by the prisms of the lens, the upper beams being directed down, and the lower beams deflected up. 2. Fluted portions of the lens direct more of the light to the near side of the road.
|
 |
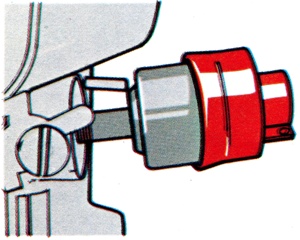
Moveable throttle stop, also known as idle-stop solenoid, which takes place of idle adjustment screw and prevents engine running on ('dieseling') when switched off. |
 |

A particular type of suspension arrangement that minimizes nose dive and tail-end lift during heavy braking. It produces a more comfortable ride as well as providing higher levels of traction. |
 |
Bearing of almost any type - ball, taper or roller. |
 |
Petrol additive designed to suppress knocking, or detonation. |
 |
Measurement of the resistance to detonation of a petrol mix when ignited in the cylinder. |
 |
Carburettor vent that opens when the throttle is closed. It releases vapour and prevents fuel from being boiled and ejected from the carburettor as a result of heat build-up when the engine is idling after a hard run. |
 |
Spring, often found in clutches and modern discbrake systems, designed to eliminate unnecessary rattle. |
 |

A suspension aid that increases resistance to body roll without giving a stiffer, less comfortable ride. The centre of the bar is attached to the underside of the body, the ends of the bar are bent through right angles and attached to the suspension control arms. U-shaped bar, with ends linked to the axle or wheel assemblies, and usually turning in rubber mountings on each side of the chassis. The suspension acts so that the body and axle remain parallel and the bar turns in its brackets, any body roll being resisted by the torsion set up by the anti-roll bar. |
 |
Sensor mechanism fitted in the braking system to prevent wheel lock and thereby reduce the danger of skidding. |
 |
System using a small passage in the carburettor to prevent fuel from being syphoned in to the engine from the float bowl. |
 |
Any device to discourage thieves. Electric devices may isolate the ignition circuit or sound the horn when the car is tampered with. Mechanical devices lock the steering, gear lever or clutch pedal. A variety of locks are obtainable for most removable articles such as wheels, spare wheels and aerials. |
 |
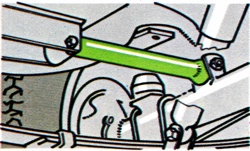
Device to stabilize leaf-sprung rear axles by reducing the tendency of the springs to wind-up, tramp and patter on maximum or heavy acceleration from a standstill.
|
 |
Chemical that lowers the freezing point of water (usually 0�C, 32 �F). It is put in the cooling system to prevent the expansion which water normally undergoes on freezing. It is often based on ethylene glycol. |
 |
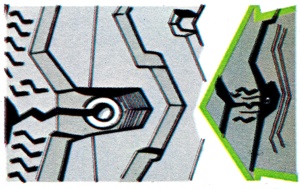
In a tyre tread, a lateral drainage channel connecting the outer water channel in the tread pattern with the edge of the tyre. It is designed to clear away water at a swift rate, thus reducing the danger of aquaplaning. |
 |
Loss of adhesion on a wet road. When a tyre fails to clear away water in front of each segment as it contacts the ground, a wedge of water builds up in front and finally forces the tyre segments clear of the road surface so that the vehicle fails to respond to steering and brakes. Where high tyre pressures and smooth tread combine, aquaplaning can take place at relatively low speeds.
|
 |
Process in which an electric arc is used as a heating agent. In the carbon arc process, a single carbon rod melts the metal being welded and a filler rod is applied as in Oxy-welding. In the metallic arc process the arc is struck and maintained with a metallic electrode which also acts as a filler rod. |
 |
Condition arising when a spark jumps the air gap between two electrical conductors. An example is arcing of a spark-plug. |
 |
The coils of wire wound on a soft iron core that forms the revolving part of a generator or electric motor. It revolves between the poles of an electro-magnet. |
 |
Name for tempered, shatterproof glass. |
 |
System in which the engine and transmission are built into a short chassis which carries a strong towing and swivelling attachment. |
 |
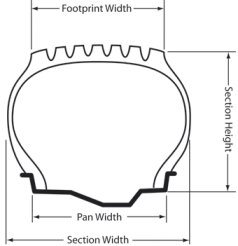
Refers to the height of the tyre expressed as a percentage of the cross-section profile. Hence a 70% aspect ratio refers to a tyre that is 70% as high as it is wide. Also defined as the ratio of the height of a tyre wall to its width. For example, the height of a 70 series tyre is 70% of its width. The lower the ratio, the wider the tyre. |
 |
Asymmetric Carcass
Tyre carcass whose composition is not uniform in cross-section. The theory is that the outer shoulder of the tyre is subjected to the greatest loads in cornering and thus has a construction different from that of the inner shoulder. |
 |
Asymmetric Tread

Tyre tread whose pattern is not uniform over its cross-section. The theory is the same as that in the case of the Asymetric carcass. |
 |
ATDC After Top Dead Centre
(see Top dead centre) |
 |
Atmospheric Pressure
The pressure exerted by air. At sea level it is 14.7 pounds per square inch or 1.0355 kilograms per square centimetre. This base pressure is referred to as an atmospheric pressure of 1, or as 1 atmosphere. |
 |
Atomizer
Device used to disperse a liquid in fine droplets as a spray. |
 |
Automatic Advance
Automatic means of varying the amount by which the ignition spark precedes top dead centre as the engine accelerates or decelerates. |
 |
Automatic Choke
Pre-set device in the carburettor to vary the fuel/ air mix according to the engine condition. A richer mix is supplied for cold starting and a weaker mix as the engine warms up. |
 |
Automatic Cut-Out

Electromechanical switch that prevents the battery from discharging through the dynamo. It usually operates when the dynamo is stationary or producing too low a supply to charge the battery. |
 |
Automatic Level Control
Suspension system which maintains the rear of the car at a predesigned level regardless of load, by compensating for any load variations. It is sometimes referred to as automatic ride control. |
 |
Automatic Transmission
Automatic alternative to the conventional clutch and gear lever transmission. It is operated by hydraulic pressure from an oil pump acting on an epicyclic gear train that is sensitive to throttle opening. Gears are changed automatically as engine load varies. Such transmissions are usually fitted with a means of holding on to one particular gear when desired. On more sophisticated models there is a manual override control which permits the driver to change gear by hand despite the absence of a clutch. |
 |
Autronic Eye
Automatic electronic mechanism to select the correct headlight beam during country driving. |
 |
Auxiliary Spring
Additional rubber spring which can be fitted to each side of the car at the rear when heavy loading is expected. |
 |
Avalanche Diode
Semi-conductor device with very high resistance to current flow at low voltage which reduces its resistance suddenly at a predetermined level as the voltage increases, allowing the current to flow. |
 |
Axle
A high grade alloy steel forging, mounted transversely, that carries the wheels and upon which the car body is supported by the road springs.
|
 |
Axle Casing
The outer casing of the driving axle assembly protecting the final drive and half-shafts. |
 |
Axle Ratio
Comparison of the revolutions per minute (rpm) of the propeller shaft, before reduction by the final drive gears, with the rpm of the driven wheels. |
 |
Axle Stand
Strong base frame with telescopic extensions capable of locking in several positions, used to support the car by an axle. |
 |
Axle Tramp
Violent 'kick' or 'patter' in leaf-sprung rear axles as a result of the springs winding up and storing energy under maximum acceleration from a standstill, then suddenly releasing it as the rear wheels lose grip and spin. |
|
|
Sell Your Car or Parts
Browse the Classifieds
It's Absolutely Free! - Find Out More
|



