|
Throughout this site we use
many technical terms, and given the breadth of readership
our site enjoys, sometimes we are remiss and incorrectly
assume everyone knows what we are referring to. For those
that do not, here are some explanations of the technical
terms use. |
 |
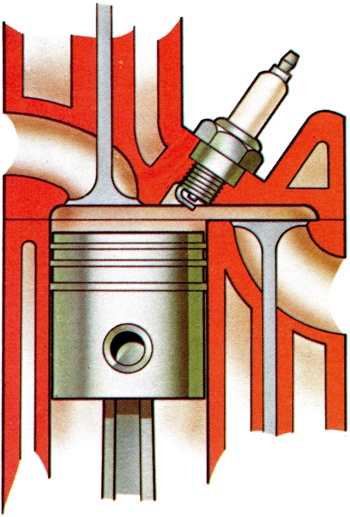
A type of cylinder head design having an overhead inlet valve and side valve exhaust in the interest of gas flow, used by eminent manufacturers in former years including Rolls-Royce. Rover engines of the 1950 era were variants. |
 |
To lose intensity, or disappear gradually, used in respect of all lighting, particularly headlamps when due to some excessive load on the system such as the use of the starter motor, a short-circuit, or failure of an older battery to provide the same voltage as the charging system when the latter cuts out, the lights visibily dim on brakes, where after repeated use, the heat generated in the brake drums or brake discs raises the temperature of metal and linings to a point where the coefficient of friction between the surfaces is seriously impaired causing loss of braking force in spite of greater pedal force on painted surfaces, where oxidation of surface film over several years, particularly with certain colours, causes loss of depth of colour.
|
 |
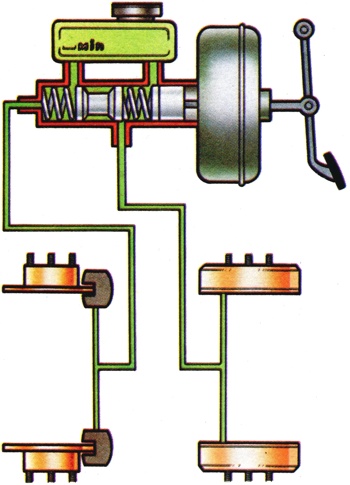
More properly called "split circuit" or "dual braking" system, in which the hydraulic system is in two isolated parts so that a rupture in any one item in the system will not render the whole of the braking system inoperative. On the simplest type the bore of the master cylinder is divided into two compartments by a floating piston. One compartment serving the front brakes and the other the rear brakes. |
 |
A device for the propulsion of air by means of a series of angled blades attached to a rotating boss. Air is drawn axially into the frontal area of the fan and expelled both axially to the rear and also outwards under centrifugal force. Thus fans are more efficient drawing air through a radiator matrix from behind, than blowing from the front of the matrix. Fans used to be cast, or fabricated from sheet metal, but now are frequently plastic mouldings. A fan is used also on an air-cooled engine and may be ducted. |
 |
The fabric-rubber endless belt which drives the cooling fan, and usually the water pump and generator or alternator, from a pulley on the nose of the crankshaft. The belt is invariably vee-section now, but on earlier cars e.g. Austin 7, was flat. |
 |
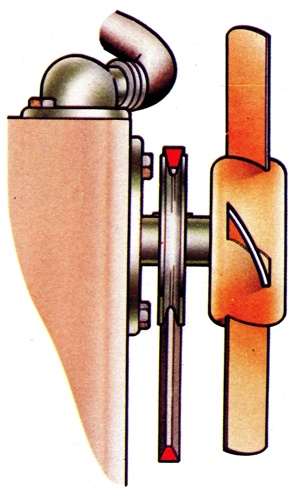
The Vee-section pulley to which the cooling fan is attached, which is usually mounted on the spindle of the water pump. Now technology has been used to develop a particular type of continuous fan belt which can be used, singly, to drive such engine ancillaries as the alternator, water pump, air-conditioning compressor, etc. |
 |
Derived from the architectural term for the weather board under the eaves of a house, this was the panel immediately under the I windscreen, in traditional car design, which accommodated instruments or an instrument panel, switches, controls and possibly compartments for driver's aids. |
 |
The name of a design for the rear end of a saloon car where the more normal stepped profile from roof line via rear window to rear boot is replaced by a smooth curve giving better aerodynamic shape, a larger and more sloping rear window, and virtually including the boot space inside the main compartment of the car (also see Hatchback). |
 |
The use of a mains operated battery charging trolley or box, sometimes called a booster, to allow a car with an exhausted battery to be re-charged quickly.
|
 |
A position of the throttle butterfly open beyond the normal idling position, set by interconnection with the choke (enrichment) control, to give somewhat higher engine speed during warming up, to preclude stalling.
|
 |
A loss of mechanical properties in a metal due to repeated reversals of stress, tensile and compression, or shear, occasioned by flexing, pressurizing of vessels or vibration. Thus a fatigued metal will fail at a much lower tensile-stress than the UTS quoted for new metal. |
 |
A strip of hardened steel of precise and uniform thickness used for measuring the gap between adjacent surfaces such as between a valve stem and tappet screw. |
 |
A sleeve of metal shrunk around the insertion end of the wooden handle of a tool to prevent splitting. Also the soft copper (or other soft metal) sleeve or ring placed around a metal pipe such as a fuel pipe and which is compressed by the union nut to produce a sealed joint. |
 |
The area of magnetic force around a magnet, whether a permanent magnet or an electro-magnet. |
 |
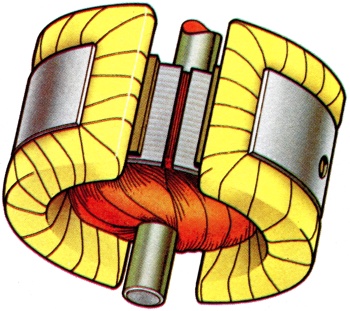
Coil of insulated copper wire surrounding a soft iron core which on energising, by supply of current, produces the necessary magnetic field in which the armature of a dynamo or motor rotates. In the former case the current supplied to the field winding controls the output current. |
 |
The terminal on a dynamo connected to one end of the field winding, identifiable as the smaller of the two terminals, and connected to the F terminal of the control box. |
 |
The fine wire of tungsten or other metal inside a lighting bulb which becomes incandescent when sufficient current passes through, and so produces light. |
 |
The closure cap to the filling orifice of a tank, radiator, or engine sump. In the case of a radiator on a modern vehicle the filler cap is provided with valves to ensure proper pressurization of the system and protection against excess pressure. |
 |
Any material added to a mix to produce necessary bulk, especially in paints and stopping materials. |
 |
A rounded filling-in of metal between two surfaces where meeting, either a concave curve deliberately machined to avoid abrupt change of section, or a convex .curve resulting from welding build-up. |
 |
A device for straining a liquid or gas to remove unwanted foreign material. It will consist of a metal gauze, cloth, or fibre, or specially prepared paper to produce the necessary degree of filtration.
|
 |
The removable cartridge of felt or paper used in a bowl type filter. |
 |
A plate of metal protruding from the main surface of the metal to increase its surface area and so expedite the flow of heat from (usually, but sometimes into) the bulk of the metal. These cooling fins are found on the external surfaces of cylinder heads and barrels of air cooled engines, also sometimes on sumps, brake drums, compressor bodies etc. |
 |
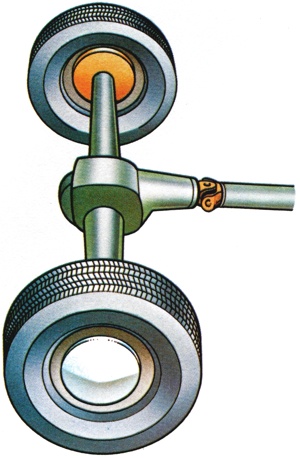
On orthodox vehicles, the final stage in the transmission of engine torque to the driving wheels in which the direction of drive line turns from longitudinal to transverse, a permanent torque multiplication is applied, by crown wheel and pinion, and the differential gear is included. |
 |
Any finger-like protrusion of metal to provide a contact with some other item. Used specifically for the rocker like levers fitted in some designs between the overhead camshaft of an engine and the valve stems to obviate side thrust on the valve stem. |
 |
The steel wall separating the engine compartment from the passenger area in a vehicle. May be a sandwich with asbestos interlay and usually features also as the scuttle or dashboard. |
 |
The ignition of the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber of an engine. |
 |
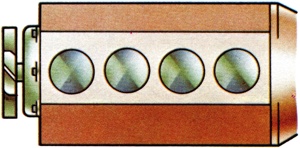
The sequence in which ignition takes place between the various cylinders in an engine starting with No.l cylinder. Thus a common sequence for a four cylinder in-line engine is 1342. |
 |
Otherwise called the primary shaft, is the input shaft of the gearbox carrying on splines the friction plate of the clutch and at the other end inside the gear box, the constant mesh pinion and the dog clutch for direct drive. |
 |
One having five forward gears, one of which is usually a direct drive. One of the indirect ratios may be an overdrive. To date this is invariably a manual box. |
 |
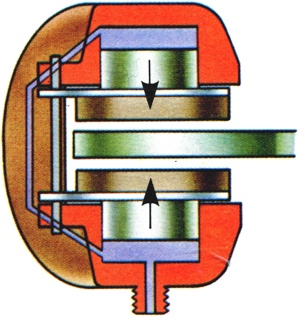
Disc brake design in which the friction pads either side of the disc are operated by individual hydraulic pistons so that there is no movement by reaction of the caliper as in the case of one cylinder swinging caliper. |
 |
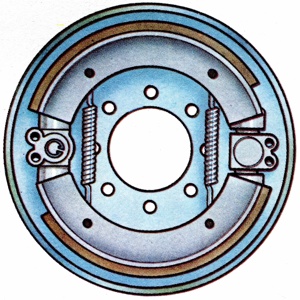
A simple design of drum brake in which the operating cam is located in one position on the back plate. |
 |
A type of coach-work, more sporty in appearance than the orthodox saloon car, usually with only two doors, the rear seats in some cases intended only for occasional use; and with a fixed roof. |
 |
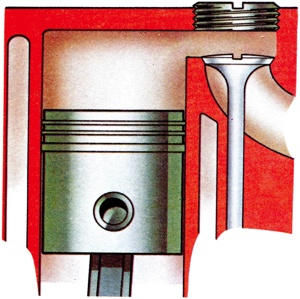
An older design of engine, particularly heavy commercial engines where the cylinder was cast complete with head, screwed inspection caps being provided for access to the side valves. |
 |
More properly called a fixed choke or open choke carburettor. A simple carburettor having a fixed choke and one or more plain jets which requires a compensating system if mixture strength is to be maintained throughout the speed range. The other class of carburettor, variable choke, with a tapered needle moving in the jet achieves a constant vacuum over the jet outlet and hence constant mixture strength. |
 |
The spread of the flame through the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber initiated at the spark plug. Mixture strength, I turbulence, temperature, and shape I of chamber all affect the rate of I flame propagation. |
 |
The extent of propagation of combustion from the I initiation at the spark plug. |
 |
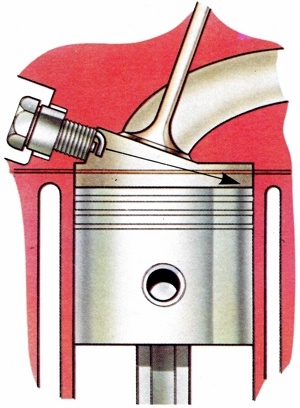
The distance the flame travels from the spark plug to the remotest part of the combustion chamber. |
 |
A minor surface at an angle, usually perpendicular to the razor surface, either for reinforcement of the edge and/or to provide attachment holes as studs for a cover or an adjacent item, or for machined mating surfaces.
|
 |
A flat plate hinged on one edge to direct air alternately to either of two ducts or shut off the flow, as used in heating and ventilating systems of vehicles. |
 |
The use on earlier cars of a flap either in the roof panel or more often in the side panel of the scuttle i.e. just behind the bonnet, to extract air as the car travelled. |
 |
Familiar term for the stalk-type spring back switch attached to the steering column permitting flashing of the headlights. |
 |
The automatic switching device which gives intermittent flashing of direction indicators by the make and break action of a bimetallic strip. |
 |
Any indicator giving warning of some state of affairs by flashing light usually controlled by a flasher unit. More specifically refers to direction indicators at the front and rear of a car as required by current legislation. |
 |
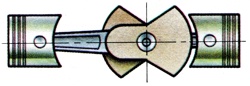
An internal combustion engine in which the pistons operate in a horizontal plane instead of the more conventional upright position. Usually has pistons operating from either side of the crankshaft that is horizontally opposed. |
 |
Flat Head Engine
See F-head. |
 |
A simple open ended spanner, either single or double ended. |
 |
Horizontally opposed four cylinder or six cylinder engines, most commonly found in the Volkswagen Beetle, Porsche and Subaru iterations. |
 |
Refers to an engine’s performance being poor in one particular part of the rev range. Can be described as a hesitation, or interruption in torque produced by the engine, due to ignition irregularity (such as high cylinder pressure causing excessive resistance at the plug gap) or carburettor failure such as temporarily weak mixture during acceleration. |
 |
Undue local wear (a worn patch) caused by uneven braking as would occur through distorted brake drum. Also refers to tyres with nylon cords which may remain distorted after a lengthy period of rest in one position. |
 |
The process of rubbing down successive coats of paint by wet-and-dry paper to obtain a perfectly smooth unblemished surface before proceeding with further coats. The flatted surface gives a key for the next coat to improve adhesion. Originally a blacksmith's term for re-establishing a surface after forging or hammer-welding, by hammering on a flatting tool. |
 |
Flexible pipes used in the hydraulic brake system between wheel hubs and chassis to permit suspension movement; made of rubber and braided fibre with metal and fittings. Also tubes of rubber on fibre reinforcement for use in the cooling system and heaters. |
 |
Probably derived from the old definition: the side of a pig, this is the side panel of the engine bay, a structural member which also forms the inner surface of the wheel arch. |
 |
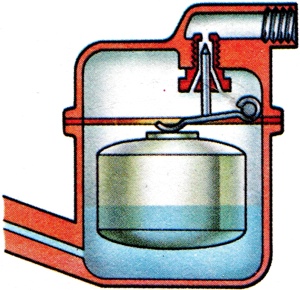
The buoyancy component of the carburettor float chamber, made from thin sheet brass usually in the form of a hollow cylinder, which operates a needle valve either directly or via a lever, which cuts off the entry of fuel when a specific level is reached in the chamber. Also the condition of some reciprocating item floating between extreme positions. |
 |
An alternative name for a float-chamber.
|
 |
The reservoir supplying fuel to the jets in the carburettor and which, by maintaining a constant level, ensures consistency of mixture strength as well as preventing leakage of fuel. |
 |
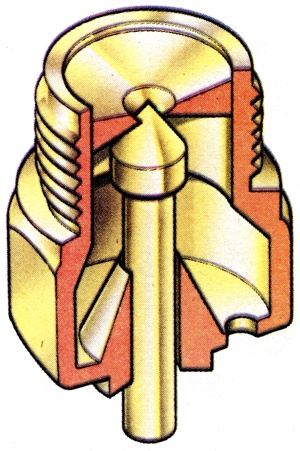
A steel pin with an accurately ground conical end which seats exactly in a brass housing thereby sealing the fuel inlet to the carburettor float-chamber when sufficient force is applied to the needle by the float. |
 |
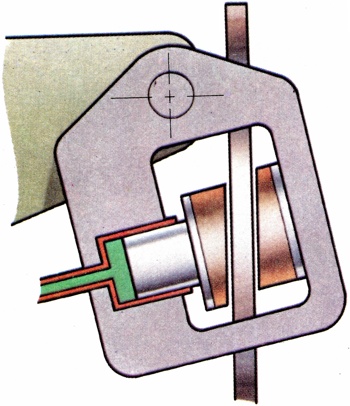
A design of disc brake in which there is only one hydraulic slave cylinder, applying the friction pad to that side of the disc, the pad on the other side being fixed to the caliper and being applied equally by reaction as the caliper swings on its mounting. |
 |
A design of cam-operated drum brake in which the cam assembly is able to move, circumferentially, a limited amount to compensate for different rates of wear between leading and trailing shoes. |
 |
A condition in which fluid is leaking from some vessel or system due to the fluid over-running a prescribed level due to failure of a level setting device such as a float mechanism or a failure or blockage in some part of a normal circulation system. |
 |
Nowadays a little used term to differentiate vehicles having gear levers in the orthodox "floor" position from those having steering column change levers. |
 |
The mild-steel pressing which includes the floor for the passenger compartment, the transmission tunnel and the rear seat structure, in a unitary type body. |
 |
a) The pattern of aerodynamic flow round an object in a stream of air. b) The grain pattern in metal consequent to forging processes or in sheet metal after rolling or spinning. |
 |
Brakes actuated by an hydraulic system. |
 |
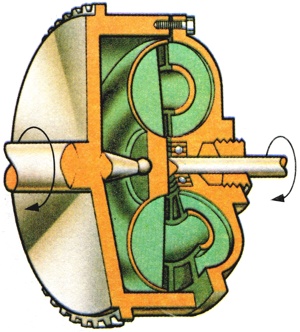
A torque transmission device using a fluid as the only connecting medium, a driven impeller accelerating the fluid centrifugally, which then expends the accumulated energy on a turbine. |
 |
A successful design of fluid coupling used for several decades by the Daimler Car Co. Ltd., in conjunction with a preselector epicyclical gearbox. Used on Daimler, Lanchester and BSA cars and Daimler and AEC buses. |
 |
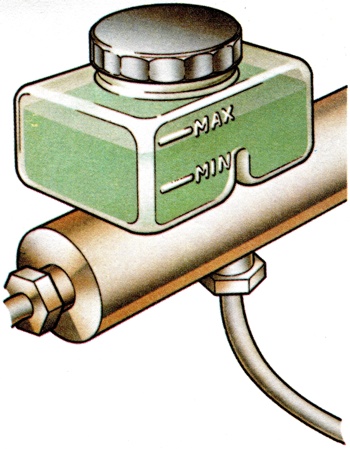
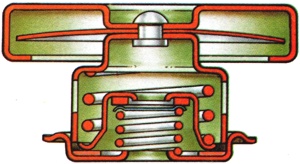
The vessel containing the necessary reserve of fluid I for a hydraulic system to prevent I injection of air and permit fluctuation I in internal capacity of the enclosed I part of the system.
|
 |
A light bodied oil used after draining an engine or gearbox, I to allow running of the engine without load thereby removing sludging and foreign matter. This oil is immediately drained out and replaced by normal lubricant. |
 |
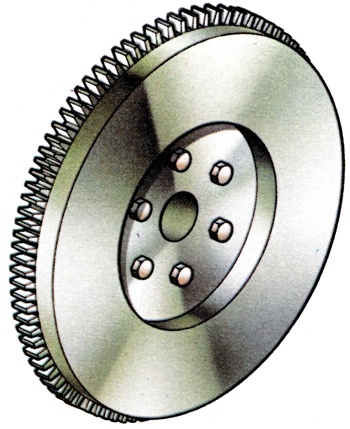
A heavy disc of metal attached to a rotating shaft which by virtue of its inertia stores some of the energy from a fluctuating torque and enables rotation to continue, thereby helping to maintain a constant speed. In the case of an automobile it is attached to the crankshaft and using some of the energy of the power I stroke enables the crank to continue rotating through the other three strokes. It also provides one driving face for the clutch and an outer ring gear for the engagement with the starter motor. |
 |
Small lines machined on the periphery of the fly-wheel to indicate the correct angle for some stage in valve timing e.g. I.V.O. for inlet valve opens, and for basic ignition setting. |
 |
A toothed ring sweated (i.e. shrunk fit) to the periphery of the fly-wheel for engagement with the pinion of the starter motor. |
 |
Auxiliary lamps, required legally to be fitted only as a symmetrical pair, having a flat topped beam designed to limit reflection from the moisture particles of fog. If fitted below a prescribed height must only be used in dense fog or falling snow. |
 |
The main braking system control by foot-pedal operating on all wheels in light vehicles. |
 |
a) The contact patch on the road made by the tyre when stationary, b) A type of adjustable wrench particularly suitable for use on pipes. |
 |
The process of shaping a piece of metal, by hammering, or pressure applied to a die, thereby producing a flattened and laminar grain structure which greatly improves the toughness of the product. Items so made, such as beam axles or steering drop arms are called forgings. |
 |
Aeronautical term based on resistance of a body to motion through a fluid (including air). |
 |
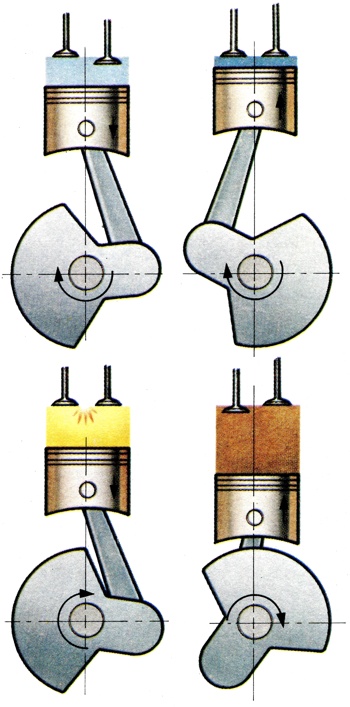
The cycle of operations for an internal combustion engine, the four strokes being induction of mixture (or air), compression, power and exhaust, thus requiring two crankshaft revolutions for each cycle. |
 |
Usually on a multi-wheeled vehicle where twin front axles have all four wheels swivelled to appropriate angles by the steering gear. |
 |

An exhaust system for a four cylinder engine in which each exhaust port has its own outlet pipe in lieu of the more usual manifold, the four pipes usually joining into pairs, or into one pipe, before reaching the first expansion. |
 |
A fixed caliper for a disc brake having four operating cylinders applying brake pads, two each side of the disc.
|
 |
A gearbox in which there is a selection of four ratios for forward travel. |
 |
A cylinder head of a four-stroke internal combustion engine, in which there are four valves to each cylinder, two each for exhaust and inlet ports. |
 |
A vehicle of four or more wheels in which it is possible to obtain driving torque on four wheels. |
 |
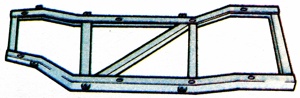
The steel frame consisting of longitudinal, cross and possibly diagonal bracings which formed the backbone of earlier motor cars and still does for heavy commercial vehicles but is superseded by monocoque or unitary construction in modern light vehicles. The chassis includes mounting points for all major components and bodywork. |
 |
A type of clutch or coupling which transmits torque only in one direction, so permitting the driven member to over-run the driving member. Used as a refinement in the transmission line of Rovers in former years, permitting the engine to slow-run while the vehicle coasted down gradients so contributing to fuel economy and to allow clutchless gear changes.
|
 |
Lost motion necessary in the articulation of a control, such as the clutch pedal, which ensures that the pedal or lever does not inhibit complete return movement of the controlled item; it allows for repositioning due to wear or thermal expansion. |
 |
The recessing or indentation of components in the bodywork of the car, which would usually be flush mounted. It is normally confined to lights and aerials on customised vehicles, but could also include units such as the fuel filler cap and the registration plates. |
 |
The trade name of a refrigerant used in older air-conditioning systems � now outlawed. |
 |
Resistance to movement between two surfaces in contact, depending on the total force normal to the surface (that is, keeping the surface in contact) and on the surface finish and materials in contact. Maximum friction between the surfaces is the product of the force maintaining contact and the coefficient of friction for those surfaces. |
 |
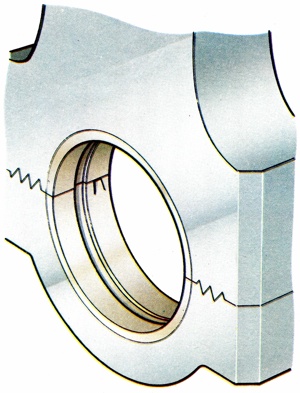
A bearing in which the moving surfaces have sliding contact such as main and big end bearings. |
 |
The difference between indicated horsepower (the power generated by the gas pressure on the pistons) and the brake power (the power measured at the fly-wheel) this difference being due also to the power required to operate valves, lubricating pumps, distributor shaft, fuel pump and other items essential to the running of the engine. |
 |
Friction material bonded to backing plates as replaceable items in a disc brake. |
 |
The centre plate of a friction clutch, a disc fitted by splines to the primary shaft of the gearbox, with annular friction linings, and clamped by spring force between the face of the flywheel and the pressure plate of the clutch assembly. |
 |
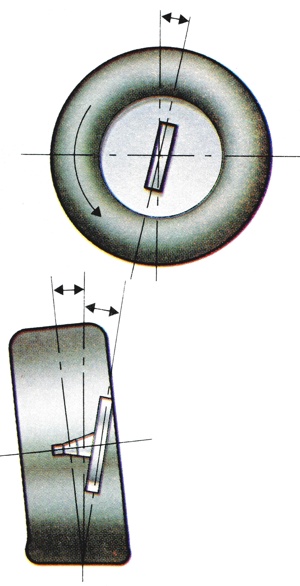
The angular relationship between the front steering wheels, their swivel axis, and the vertical, thus including king-pin inclination, castor angle, camber, toe in when straight ahead, and toe out when on full lock. |
 |
The mild steel pressing at the front of a car, accommodating the radiator grill or aperture and usually the headlamps, and supplying hinge points or catch points for the bonnet. |
 |
Abbreviated to FWD, refers to a car in which the front wheels rather than the rear are driving the wheels. Use of the front (steering) wheels for driving the vehicle instead of the more orthodox rear driving wheels. Pioneered by such firms as Cord and Alvis pre-war and exemplified during the 1960s and 1970s by the Mini, Morris 1100, Allegro, Audi and others. |
 |
The front surface of a vehicle that presents an obstruction to the airflow past the vehicle at speed. Used in conjunction with the coefficient of drag to determine the aerodynamic efficiency of a vehicle. |
 |
The source of heat energy required for any heat engine, usually petrol or diesel oil for the internal combustion engine, but including blends of other hydrocarbons such as alcohols.
|
 |
Oils or chemical compounds added to the basic fuel for the better functioning of the engine, such as tetra-ethyl lead to raise the octane value and lessen the chance of detonation. |
 |
A galvanic cell in which the oxidization of a fuel is utilized to produce electricity (a dry battery). |
 |
The tendency of fuel droplets in the air/fuel mixture drawn from the carburettor to lag behind the air during acceleration. Also the tendency of fuel to condense on the cold metal of the induction system during cold starts. Thus fuel is "dropping out" of the mixture. |
 |
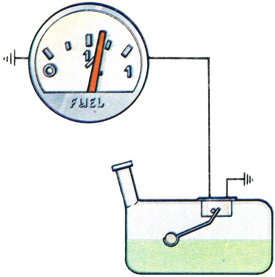
An instrument fitted to the instrument panel with a transmitter fitted to the fuel tank to keep the driver informed of the fuel contents available. On modern cars it usually consists of a float mechanism, the position of which is transmitted electrically to an instrument on the fascia.
|
 |
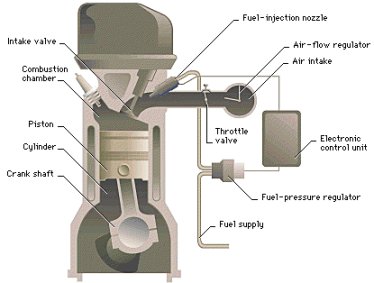
A system where petrol is metered in accurately measured quantities directly into the cylinders, rather than being mixed with air and drawn into the cylinders by the manifold vacuum as it is with a conventional carburettor set-up. The supply of fuel to the combustion chamber or to points in the induction manifold adjacent to the inlet valves by a metering pump, instead of the more usual supply of fuel to the inducted air via a carburettor. Greater accuracy in meeting the true requirements of the engine under any operating circumstances can be claimed. |
 |
The mixture of fuel vapour and air supplied to the cylinders of the engine, normal mixture strength being by weight about 1 to 14, but richer for starting and acceleration, and leaner for economical cruising. Combustion limits are approximately from 1:1 to 1:20 by weight. |
 |
An atomizing valve which delivers fuel in a fine, balanced spray to the combustion chamber or induction manifold when supplied at the correct time and volume by the fuel pump in a fuel injection system. |
 |
A pressure regulator essential to most fuel injection systems to limit the pressure of fuel supplied from the supply pump to the injection pump. |
 |
Electrical or mechanical device that delivers fuel from the fuel tank to the carburettor. A diaphragm type pump either mechanically-operated from the camshaft or electrically-powered to supply petrol to the carburettor or injection system. |
 |
An unacceptably weak mixture due to failure of the carburettor or injection system to supply the requisite amount of fuel, due lo impediment in ducts or jets, pump failure or empty fuel tank. |
 |
Mild-steel or plastic pressings forming a reservoir for fuel, usually at the rear of the car, equipped with suitable venting pipes, draining plug and fuel contents transmitter. |
 |
Vaporisation of fuel in any part of the system caused by local high temperature and perhaps resulting in a vapour lock. Especially in tropical climates it is necessary to lag pipes adjacent to exhaust pipes and shroud the carburettor from manifold temperature by an aluminium plate. |
 |
A part of a diaphragm spring clutch about which the fingers of the diaphragm spring obtain a fulcrum to release the clutch. |
 |
A filter for the engine lubricating oil which is fitted between the pump and the delivery gallery and thus filters all the oil passing from the pump. The alternative by-pass filter deals only with that small proportion of the pump's delivery passing through a meter orifice, but can, with safety, produce a much finer degree of filtration. |
 |
The maximum angle that the front wheels can swivel either side of the straight-ahead position, usually determined by adjustable stops. |
 |
A design of gudgeon pin which is free to move axially in the piston bosses and small end of the con-rod and fitted with brass end pads to protect the cylinder bores. |
 |
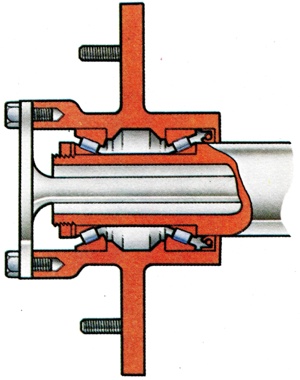
A design of the hub for the driving wheels in which weight and side loads are entirely taken on double ball or roller races and thereby the half-shaft merely transmits the driving torque. Although still found on some commercial vehicles it is not used in modern private cars. |
 |
A soft wire, usually held in a glass tube or cartridge with metal end caps, which melts if the current passing is excessive. |
 |
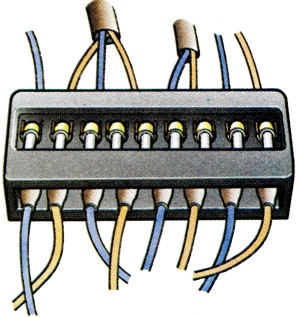
A box containing a number of fuses for different circuits at one point for convenience of access and replacement. |
 |
A larger fuse, possibly a metal strip, in the main circuit from the battery, protecting the battery and the wiring between the battery and the fuse box in the event of damage to insulation in that area. |
|
|
Sell Your Car or Parts
Browse the Classifieds
It's Absolutely Free! - Find Out More
|



